DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. When replication mistakes are not correcte they may result in mutations, which sometimes can have serious consequences. This process—nick sealing-requires energy, provided by the breakdown of ATP to AMP and PPi. It participates in the DNA repair process.

Supercoils and DNA topoisomerases: As the double helix of DNA separates from one side and replication proceeds, supercoils are formed at the other side. Enzymes of base excision repair : GEL PL ease = G lycosylase, AP-E ndonuclease, L yase, DNA P olymerase, DNA L igase Excision repair occurs in the Gphase of the cell cycle. DNA mismatch repair occurs in the S phase of the cell cycle. What is enzyme uses RNA to make copy of DNA? Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Repair mechanisms correct the mistakes. The replication enzyme needs to make a long enough chain to replicate the entire chromosome. The repair enzyme needs only to make a long enough strand to replace the damaged sequences in the chromosome. The best‐studied bacterium, E. Mismatch repair One class of DNA repair system.
Recognizes and removes mutations that result from base-pairing that is not complementary. Lipase is the general name for an enzyme that breaks down lipids. Ligase joins the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand of the DNA during replication. It catalyzes the covalent addition of deoxyribonucleotides to the 3′-OH of a preexisting nucleotide called as primer. MMR enzymes excise an incorrect nucleotide from the daughter DNA and repair the strand using W-C pairing and the parent DNA strand as the correct template.
So living creatures must have elaborate DNA repair machinery. DNA replication : The process by which DNA is copied in a cell. University of Chicago biologist James Shapiro points out that:all cells from bacteria to man possess a truly astonishing array of repair systems which serve to remove accidental and stochastic sources of mutation. In addition, recombinational repair systems act to allow one copy of the replicating DNA at a replication fork to supply information to the other daughter chromosome.
Finally, interrupting the catalytic cycle of enzymes that utilize a covalent protein- DNA intermediate, such as topoisomerases, also generates DPCs that often are removed by replication -coupled repair mechanisms. DNA glycosylases recognize and remove damaged bases from DNA by cleaving the base–sugar (N-glycosylic) bon and downstream base excision repair enzymes restore the correct nucleotide. DNA bases are chemically reactive and are continuously subject to damage by mechanisms including alkylation, deamination, oxidation, and ultraviolet radiation.
Post- replication repair is a type of excision repair. Successful post replication repair depends on the ability of enzymes to distinguish between old and newly replicated DNA strands. DNA repair , any of several mechanisms by which a cell maintains the integrity of its genetic code. DNA repair ensures the survival of a species by enabling parental DNA to be inherited as faithfully as possible by offspring.
It also preserves the health of an individual. This mechanism is called DNA repair. A failure to repair DNA produces a mutation. The DNA polymerase would be unable to carry out error-checking. In yet another type of repair , nucleotide excision repair , a damaged base is removed along with a few bases on the 5′ and 3′ en and these are replaced by copying the template with the help of DNA polymerase.
There are three modes of excision repair , each of which employs specialized sets of enzymes. DNA continually undergoes a process of replication and division and. In normal double-stranded DNA , A pairs with T and G pairs with C. Nucleotide excision repair corrects. It adds new nucleotides to the DNA helix.
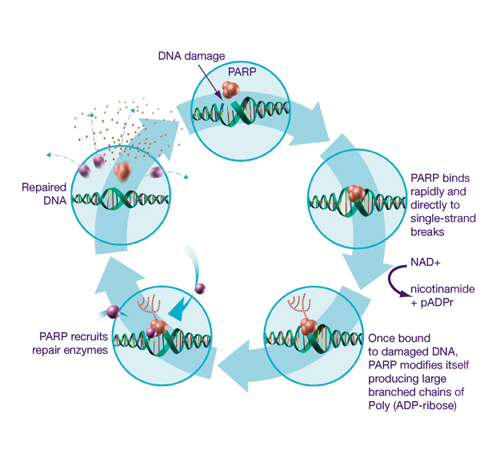
It forms bonds between DNA nucleotides. It separates DNA strands 2. Which enzyme removes the RNA primer during replication ? The diagram below shows a short section of DNA molecule before and after.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.