
Most sand is made of quartz, which is largely silicon oxide. What type of soil is sand? Physically, sand is made up of tiny , loose grains of rocks or minerals that are larger than silt but smaller than gravel. Its composition directly affects its color, resulting in black, white, pink and green coloring.
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles. The sand particles consist of small grains of silica (SiO ). These properties are what help us differentiate between different types of soils or sediments. Normally, there are types of known soils: sand , clay and silt. To judge the quality of the available sand , one must know the properties of good sand.
Before using sand in a project, these desirable properties must be ensured. Sand is a mixture of small grains of rock and granular materials which is mainly defined by size, being finer than gravel and coarser than silt. The grains should be sharp , angular and coarse. The sand should be free from clay material and organic matters.
It should be free from salts. Flowability The ability of moulding sand to behave like a fluid when it is rammed is called flowability. Collapsibility The ability. Sand is created from fragments of items like quartz and sand does not absorb water and is not soluble in water.
Sand is porous and allows air to pass freely through it. The gradation of grains size should be such as that it will give minimum voids. The finer the sand grains, the finer is the molding sand as whole. Fine grain sands give good surface finish but possess low permeability. Characterizing Properties of Sand Remember that sand is actually a size of sediment Characterizing Properties of Sand Composition Particle size distribution Surface Texture Roundness and Sphericity Characterizing Properties of Sand Composition While sand typically is made up of Quartz (SiO2) it can in fact be composed of almost any mineral or combination of minerals or even sand sized fragments of rocks Characterizing Properties of Sand Particle Size and Distribution The source rock and.

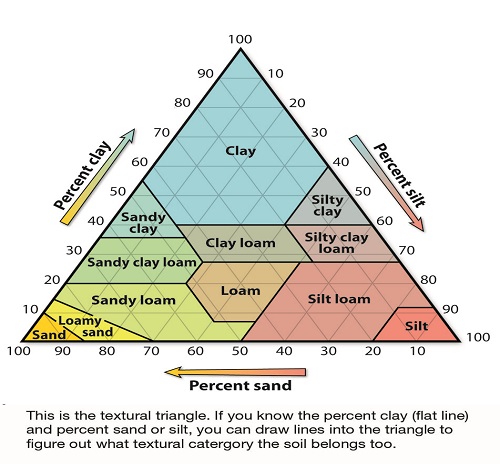
Sand particles are the largest and clay particles the smallest. Most soils are a combination of the three. The relative percentages of sand , silt, and clay are what give soil its texture. A clay loam texture soil, for example, has nearly equal parts of sand , slit, and clay. The size of its particles is large.
Fewer large particles can occupy the same volume of soil so there are fewer pores and less porosity. Compaction decreases porosity as bulk density increases. If compaction increases bulk density from 1. Sand or gravel aggregate has an R-valueof about 0. Some sources quote a much higher R-value for sand and gravel aggregate but you need to look at the thickness or amount of sand or gravel when you see such quots. Properties of Building Materials For a material to be considered as building material, it should have required engineering properties suitable for construction works. Characteristics of sand and criteria for its comminution From construction material to semiconductor technology On planet earth sand is a very common unconsolidated sedimentary rock.

Sand is formed from rocks broken down through weathering. Consequently, it is gritty and coarse and lends this. Of the three main soil types, sand is the largest, large enough that you can see the individual particles of sand.
Zircon requires less binder than. The colour of the sand soil is yellow. It has the fastest and greatest drainage of the water. As fineness modulus of sand changes from 2. On the other hand by increasing Fineness Modulus from 2. Compressive strength increases from 49.
MPa resulting in increase in strength. The volumetric clay content in the samples varied from to 1. It is weekly composed (loose). The total porosity at MPa differential pressure is plotted versus the volumetric clay content below. However, its effect on the modulus of elasticity is minimal.
Using adhesive with fine sand increased the ultimate load bearing capacity, ductility, stiffness and toughness of the reinforced concrete beams strengthened by CFRP. Salt, also called sodium chloride, mineral substance of great importance to human and animal health, as well as to industry. The mineral form halite, or rock salt, is sometimes called common salt to distinguish it from a class of chemical compounds called salts.
Learn more about salt in this article.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.