Read Clinical Trial Studies About A Treatment That May Help Your Patients. Explore Safety And Efficacy Information Along With Clinical Trial Data. Find Out Eligibility. They May Pay As Little As $35.
Learn About The Savings Card Now! Medication Information. Test for Eradication of H. How to stop H pylori? What can I expect after H. Analysis of a blood sample may reveal evidence of an active or previous H. During a breath test, you swallow a pill, liquid or pudding that contains tagged carbon molecules.
See full list on mayoclinic. Drugs that can suppress acid include: 1. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). These drugs stop acid from being produced in the stomach. See your primary care doctor if you have signs or symptoms that indicate a complication of H. Your doctor may test and treat you for H. We compared the recommendations of these guidelines , reconciled them, and addressed the increasing resistance of H pylori to antibiotic therapy regimens. The guidelines recommend bismuth quadruple therapy for first-line treatment , replacing clarithromycin-based triple therapy.
The incidence and prevalence of the disease are generally higher among persons born outside of North America. Within North America, it is more common in immigrants and in certain racial groups. Hispanic whites than among other groups such as blacks, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Alaska Natives). Any patient who tests positive for H. All patients with active or previous peptic ulcer disease should be tested for H. Patients with low-grade gastric mucosaassociated lymphoid tissue lymphoma or a history of endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer should also be tested.
If a patient with gastroesophageal reflux disease is tested and found to have H. Based on low-quality evidence, the ACG also recommends testing for those initiating long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy, those with unexplained iron deficiency anemia, and adults with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ideally, tests that identify active infection, such as a urea breath test, fecal antigen test, or endoscopic biopsy, should be used in the diagnosis of H. Nonendoscopic testing is an option in patients younger than years with uninvestigated dyspepsia without red flags. If endoscopy is used in patients with dyspepsia, gastric biopsies should be performed. If successful, cultural methods include agar dilution, disk diffusion, and the E-test.
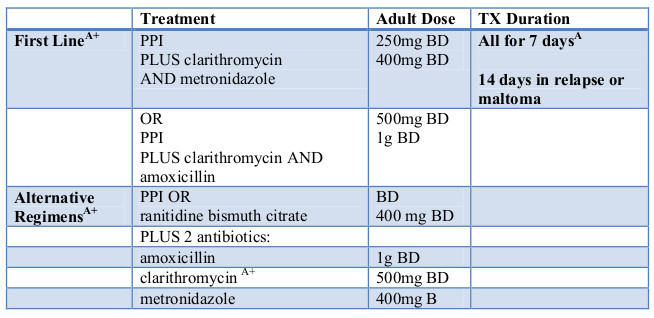
Molecular tests, such as polymerase chain reaction or fluorescently labeled nucleic acid hybridization, are faster, simpler alternatives to culture. Food and Drug Administration. However, molecular testing for H. Patients should be asked about previous antibiotic exposure to help guide the treatment regimen. The authors used the terms recommended and suggested to express their preferences. There is no regimen with a 1 cure rate for H. Clarithromycin triple therapy consists of a PPI, clarithromycin (Biaxin), and amoxicillin or metronidazole (Flagyl) for days.
Clarithromycin should be avoided in locations where resistance is greater than and in patients with any previous macrolide exposure. It may be a particularly good option in patients with macrolide exposure or who are allergic to penicillin. Although metronidazole resistance impacts the effectiveness of this regimen, it is not nearly as profound as with clarithromycin triple therapy. Bismuth quadruple therapy should be strongly considered as first-line treatment where clarithromycin resistance is high or in patients with any previous macrolide exposure.

Limited data show that the effects of clarithromycin resistance with this regimen are less than with clarithromycin triple therapy. Sequential therapy consists of a PPI and amoxicillin for five to seven days followed by a PPI, clarithromycin, and a nitroimidazole for five to seven days. Extending sequential therapy to days may improve eradication rates, but more studies are needed. The complexity of sequential therapy may limit its use. Hybrid therapy, a cross between sequential and concomitant therapies, consists of a PPI and amoxicillin for seven days followed by a PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and a nitroimidazole for seven days.
Although randomized controlled trials showed hybrid therapy to be similar to concomitant therapy, the complexity of hybrid therapy may limit its use. Levofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone with in vitro antimicrobial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including H. The few data that exist suggest that fluoroquinolone resistance may be as high, if not higher, than clarithromycin resistance in North America. Determinants of success can be related to patient factors or to the infection.
The main determinants are choice of regimen, patient adherence to a multidrug regimen with frequent adverse effects, and the sensitivity of the H. The number of doses per day and the severity of adverse effects influence treatment adherence. It is important for physicians to discuss the benefits and challenges of therapy before beginning the regimen. Other patient factors, such as cigarette smoking, diabetes mellitus, and genetics, may also have a role in treatment failure.
Of the infection-related factors, antibiotic sensitivity was found to be the most important determinant of treatment success in clinical trials and population-based studies. Data on resistance are scarce. Resistance to amoxicillin, tetracycline, and rifabutin (Mycobutin) is rare. More research is needed to determine local, regional, and national patterns of H. If infection persists after treatment , the same antibiotics should be avoided when retreating the patient.

A regimen containing clarithromycin or levofloxacin is preferred for patients who initially received bismuth quadruple therapy. Like first-line therapy, the ACG recommendations for salvage therapy are based on empiric selection rather than of culture and antimicrobial sensitivity testing. The lack of knowledge on H. United States is in sharp contrast to other parts of the worl creating a barrier to evidence-based treatment recommendations. A urea breath test, fecal antigen testing, or biopsy-based testing should be used to determine treatment success. Because of the declining success rate of H. Although the recommendation for posttesting is intuitive, the scientific evidence regarding the cost-effectiveness of such testing is lacking, except for the scenario of bleeding peptic ulcers.
Amoxicillin is an important component of H. Allergy testing may be considered after one or two failures of first-line therapy. Most often, a true penicillin allergy will be exclude and amoxicillin-containing salvage therapy can be initiated safely. In a separate in vitro study, the anticancer compound 3- bromopyruvate was also observed to have some activity against H py-lori.

A Japanese series of three cases reported successful eradication of a resistant strain with the herbal medicine, goshuyuto. We reviewed guidelines developed by expert groups in Europe, Canada, and the United States for the treatment of H pylori infection. Helicobacter Pylori ( H. pylori ) Primary Care Pathway No Negative Positive 4. A number of interesting studies looked this year at the role of triple therapy in contemporary H pylori eradication treatment. This guideline is in overall agreement with the recently published Toronto Consensus for the treatment of H pylori infection in adults, which had a narrower focus and was restricted only to treatment options. Both guidelines attempt to restrict the use of clarithromycin triple therapy and strengthen the role of bismuth quadruple therapy and.
Infection: ACG Updates. Economical, Validated ELISA kits for Diverse Species and Applications.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.