How does DNA get damaged? What is DNA repair process? Mechanisms of DNA Damage , Repair, and Mutagenesis. However, robust DNA repair and damage-bypass mechanisms faithfully protect the DNA by either removing or tolerating the damage to ensure an overall survival. Damage to cellular DNA is involved in mutagenesis and the development of cancer.
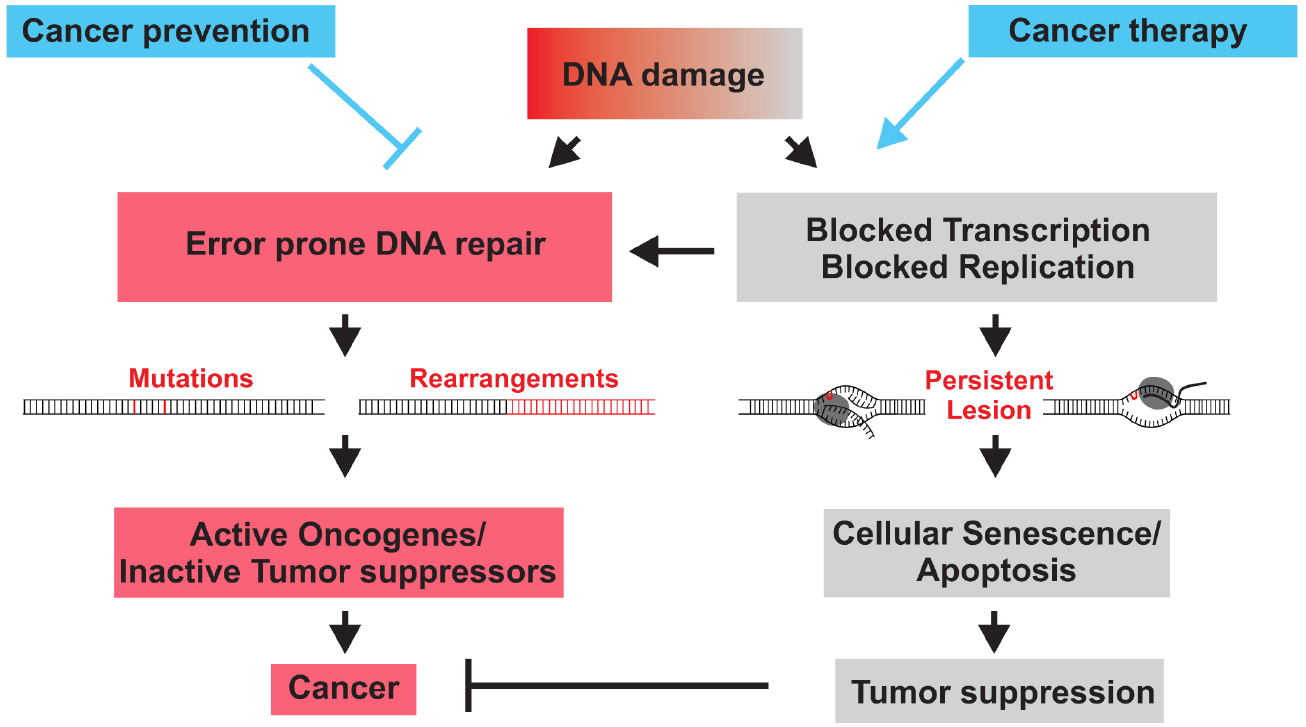
The DNA in a human cell undergoes several thousand to a million damaging events per day, generated by both external (exogenous) and internal metabolic (endogenous) processes. Changes to the cellular genome can generate errors in the transcription of DNA and ensuing translation into proteins necessary for signaling and cellular function. Genomic mutations can also be carried over into daughter generations of cells if the mutation is not repaired prior to mitosis. Once cells lose their ability to effectively repair damaged DNA , there are three possible responses (see Figure 1). The cell may become senescent, i. See full list on sigmaaldrich.
For many years, exogenous sources of damage have been thought to be the primary cause of DNA mutations leading to cancer. DNA can be attacked by physical and chemical mutagens. UV radiation produces covalent bonds that crosslink adjacent pyrimidine (cytosine and thymine) bases in the DNA strand. Ionizing radiation (X-rays) initiates DNA mutations by generating free radicals within the cell that create reactive oxygen species (ROS) and result in single-strand and double-strand breaks in the double helix.
While the cell is able to evolve into either an apoptotic or senescent state, these actions are performed as a last resort. The reaction is not a catalytic (enzymatic) reaction but is stoichiometric (chemical), consuming one molecule of MGMT for each adduct removed. Cells that have been engineered to overexpress MGMT are more resistant to cancer, likely because they are able to negate a larger amount of alkylating damage. A recent study by Niture, et al.
DNA polymerases such as polymerase-δ contain proofreading activities and are primarily involved in replication error repair. When an error is detec. Base excision repair (BER) involves multiple enzymes to excise and replace a single damaged nucleotide base.

The base modifications primarily repaired by BER enzymes are those damaged by endogenous oxidation and hydrolysis. A DNA glycosylase cleaves the bond between the nucleotide base and ribose, leaving the ribose phosphate chain of the DNA intact but resulting in an apurinic or apyrimidinic (AP) site. Oxoguanine DNA glycosylase I (Ogg1) removes 8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG), one of the base mutations generated by reactive oxygen species. Polymorphism in the human OGGgene is associated with the risk of various cancers such as lung and prostate cancer.
N-Methylpurine DNA glycosylase (MPG) is able to remove a variety of modified purine bases. The AP sites in the DNA that result from the action of BER enzymes, as. Double-strand breaks in DNA can result in loss and rearrangement of genomic sequences. These breaks are repaired by either nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) or by homologous recombination (HR), also called recombinational repair or template–assisted repair. This mechanism requires the presence of an identical or nearly identical sequence linked to the damaged DNA region via the centromere for use as a repair template.
Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) is used at other points of the cell cycle when sister chromatids are not available for use as HR templates. In order to block this survival mechanism within cancer cells, clinical trials are now being performed using inhibitors to specific DNA repair enzymes, including MGMT, PARP, and DNA -PK. The repair mechanisms such as, photoreactivation, base excision repair , nucleotide excision repair and mismatch repair , only the damaged strand of the DNA duplex is repaired and the undamaged strand acts as the template strand. However in double strand break repair and homology directed repair, both the strands of a DNA duplex are repaired.
Immediately after DNA synthesis, any remaining mispaired bases can be detected and replaced in a process called mismatch repair. If DNA gets damage it can be repaired by various mechanisms, including chemical reversal , excision repair , and double-stranded break repair. Replication stress is observed in preneoplastic cells due to increased proliferation signals from oncogenic mutations.
DNA repair mechanisms include direct repair , base excision repair , nucleotide excision repair , double-strand break repair , and cross-link repair. International Journal of Inflammation Invites Papers on the Cell Biology of Inflammation. Join Leading Researchers in the Field and Publish With Us.
Submit Your Manuscript. Direct Reversal of DNA Damage The simplest and most accurate repair mechanism is the direct reversal of damage in a single-step reaction. Here we review mechanisms of DNA repair , specifically how DSBs can be repaired either by nonhomologous end-joining mechanisms or by several homologous recombination pathways including single-strand annealing. The repair of DNA typically involves several steps.
Depending on the type of damage inflicted on DNA‘s double helical structure, a variety of repair strategies have evolved to restore lost information. Which of the following DNA repair mechanism is known as the ‘cut and patch mechanism ’? Nucleotide excision repair c. DNA helicase enzyme involved in base excision repair mechanism is_____. DNA damage can also be repaired by a combination of enzymes.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.